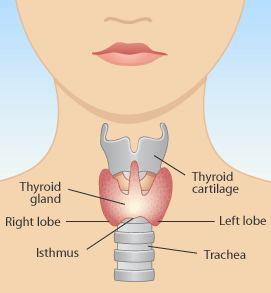
 Thyroid cancer is a disease in which tumors (malignant cells) are found in the tissues of the thyroid gland. The thyroid is at the root of throat and has two lobes, one right and one left and makes important hormones that help regulate metabolism (among other things). People that have been exposed to large amounts of radiation or who have undergone radiation treatment for health problems in the head and neck have a higher risk of thyroid cancer. Thyroid cancer is more common in women than in men the cancer may not occur until 20 years or more after radiation treatment.
Thyroid cancer is a disease in which tumors (malignant cells) are found in the tissues of the thyroid gland. The thyroid is at the root of throat and has two lobes, one right and one left and makes important hormones that help regulate metabolism (among other things). People that have been exposed to large amounts of radiation or who have undergone radiation treatment for health problems in the head and neck have a higher risk of thyroid cancer. Thyroid cancer is more common in women than in men the cancer may not occur until 20 years or more after radiation treatment.
To test for thyroid cancer, tissue is examined under a microscope to see if it contains cancer. The doctor may take a small amount of tissue thyroid. If no symptoms, the doctor feels the patient’s thyroid and check for lumps in the neck. For this, a small needle is inserted into the thyroid at the base of the throat and some tissue is taken is called out. A doctor should be seen if a lump or swelling on the front neck or other parts neck. Your doctor may order blood tests and special tests to determine whether a nodule in the thyroid makes too many hormones.
Family members, including young children who do not have cancer but who have this abnormal gene, may reduce the risk of medullar thyroid cancer developing from surgery to remove the thyroid gland (thyroidectomy). If medullar thyroid cancer is found, the patient may be born with a certain abnormal gene which may have led to cancer. Tests were developed to determine who has the genetic defect long before all members appear. Family cancer may have also inherited this abnormal gene. An abnormal was found in patients with certain types of thyroid cancer. papillary, follicular, a plastic and medullar. The genes of our cells carry hereditary information from our parents.
It is important that patients and their families (children, grandchildren, parents, brothers, sisters, nieces and nephews) see a doctor about tests that show whether the abnormal gene is present. The chance of recovery (prognosis) depends on the type thyroid cancer, if only for the thyroid or spread to other parts of the body (stage), and the patient’s age and general testing are confidential health. These can help patients and medical help.
Side effects can not be the same for each person, and may even change from one session next. These side effects of treatment depend on many factors including the type and magnitude of the effect treatment. Thyroid not always has symptoms, so it can be difficult to detect and treat diagnose. Before begins, the health care team will explain possible side effects and suggest ways to help the patient deal. The NCI provides helpful booklets about cancer treatments and tips for dealing with side effects such as radiation and You, Chemotherapy and You, and to eat Patients. Because cancer treatment can damage cells and healthy tissues, unwanted side effects sometimes occur.
However, some patients may have a rash or lose some hair during the first months of hormone pills treatment. Thyroid effects rarely cause secundarios. The level of thyroid hormone is too low, the patient may gain weight, feel of hair. It skin cool and dry can also cause chest pain, cramps, your doctor may call this anddiarrhea. Your doctor may call this condition doctor hyperthyroidism. The will closely monitor the levels of thyroid hormone in the blood during follow-up visits. If necessary, the physician to adjust the dose to the patient’s right amount. Too much thyroid hormone may cause patients to lose weight and feel hot and sweaty.
External radiation therapy may cause patients to become very tired as continues. In treatment occurs when patients receive external beam radiotherapy, it is clear that their skin becomes red, dry and painful chemotherapy given area. If treated at the same time, worsen. The side effects doctor can suggest ways to alleviate these problems. When the neck is treated with external beam radiation, patients may feel hoarse or have trouble swallowing. Other side effects depend on the area of the body which is treated. Resting is important, but doctors usually advise patients to try to stay as active when they can.
No Comments Yet